In a digitally connected world, securing your network is no longer optional — it’s essential. Every device, server, and user that connects to your network opens a door that cyber threats can exploit. That’s where network security steps in. Understanding the basics of network security helps protect sensitive data, maintain operational continuity, and safeguard user privacy.
What is Network Security?
Network security refers to the combination of policies, procedures, tools, and practices designed to protect the integrity, confidentiality, and accessibility of computer networks. It prevents unauthorized access, data breaches, misuse, and disruptions by applying multiple layers of protection across the network infrastructure.
Why Network Security is Important
From small businesses to large enterprises, every organization relies on secure networks to function. Here’s why network security matters:
- Protects Sensitive Data: Prevents leakage or theft of financial, personal, or business information.
- Maintains System Integrity: Ensures data remains accurate and untampered.
- Secures Communication: Keeps internal and external communications safe from eavesdropping.
- Prevents Downtime: Shields networks from attacks that could disrupt business operations.
- Meets Compliance Requirements: Aligns with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS.
Key Components of Network Security
A robust network security setup includes various tools and strategies, including:
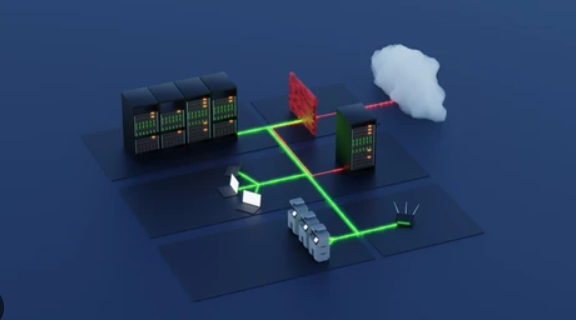
- Firewall: Monitors incoming and outgoing traffic, acting as a gatekeeper for network access.
- Antivirus & Anti-malware: Scans and removes malicious software from devices and systems.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): Detects and stops suspicious network activity.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): Encrypts data during transmission, especially over public networks.
- Access Controls: Limits access to network resources based on user roles and permissions.
- Encryption: Converts data into unreadable code to prevent unauthorized access.
Common Network Threats
Understanding what you're protecting against is crucial. Here are some of the most common threats to network security:
- Phishing Attacks: Fake emails or websites trick users into revealing sensitive data.
- Ransomware: Malicious software that locks files and demands payment to unlock them.
- DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service): Overloads a network with traffic to make services unavailable.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: Hackers intercept data between sender and receiver.
- Insider Threats: Employees or partners misusing their access privileges.
- Unpatched Vulnerabilities: Exploiting outdated software to gain access to systems.
Best Practices to Strengthen Network Security
Implementing the following strategies can significantly improve network protection:
- Regular Software Updates: Keep all systems and applications up to date with security patches.
- Strong Password Policies: Enforce complex passwords and change them regularly.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Adds an extra layer of login security.
- Network Segmentation: Divide the network into zones to limit access and reduce attack surface.
- Employee Training: Educate staff on recognizing phishing, malware, and social engineering attacks.
- Backup Strategy: Regularly back up critical data to prevent loss in case of an attack.
Types of Network Security
There are several types of network security solutions that organizations use depending on their needs:
- Cloud Security: Protects cloud-based infrastructure and applications.
- Wireless Security: Secures Wi-Fi networks from unauthorized access.
- Email Security: Filters harmful attachments and links from emails.
- Endpoint Security: Protects individual devices (laptops, phones, etc.) on the network.
- Application Security: Ensures software and applications are secure from design to deployment.
Conclusion
Network security is not just a technical requirement — it’s a strategic necessity. Whether you’re managing a home office, a corporate IT environment, or a cloud-based business, implementing strong network security practices is vital to protect your data, users, and reputation.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, staying informed and proactive about your network's safety can make the difference between resilience and disaster. By understanding the basics, investing in the right tools, and promoting a security-first culture, you can significantly reduce risk and create a safer digital environment for everyone connected to your network.